Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Operational Models
Overview
The Passport PaaS platform supports multiple merchant hierarchy models to accommodate various commercial and operational structures. This document describes the three common models used by organizations and their customers: Merchant Brand Mode, Semi-centralized, and Aggregator.
Summary Table
| Model | Account Owner | Who Payeer See as Owner (Bre-B Key Resolution) |
|---|---|---|
| Merchant Branch | Each branch/location | The branch/merchant name |
| Semi-centralized | Merchant per brand; platform can manage centrally | Merchant brand |
| Aggregator | Aggregator Entity | Aggregator Entity |
These models are examples, and you can mix different models based on your operational structure and strategy.
Key Resolution
The key resolution is a required step during payment in Bre-B. It occurs once the payment is started, either through a Key-to-Key transaction or QR codes:
- When the payer enters the Bre-B key in their banking app, the key will be resolved and the owner's details will be shown for transparency on where the funds are going.
- When the QR code is scanned in the payer's mobile banking app, Bre-B requires a Key linked to the QR code, and the key resolution is done, showing the account owner's details.
The Operational Model will affect the user experience because the account owner's details will be sent to the payeer.
Supported Merchant Models
Merchant Branch Mode
In this model, merchants have the flexibility to select either a single account or individual accounts for each of their sub-merchants. For instance, as illustrated below, a merchant may operate under a main brand while managing each branch distinctly, with each location linked to its own dedicated merchant account. This approach allows for tailored financial management and reporting, ensuring that each branch can operate autonomously while still being part of the overarching brand.
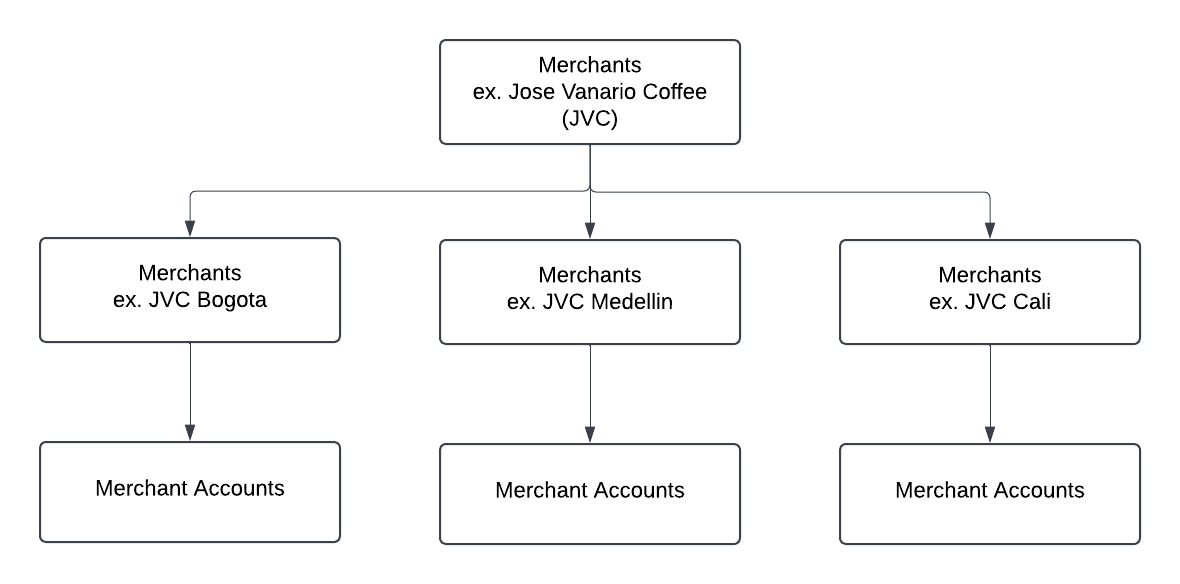
Decentralized Model Diagram
Example: Decentralized Model
- Each merchant branch is onboarded as a separate entity.
- Each has its own Merchant Account and settlement flow.
- Useful when each location operates independently and requires autonomy in reporting, reconciliation, and operations.
Implementation Notes
- Create a merchant entity per location using the Create Customer endpoint.
- Link a dedicated merchant account using Link Account.
- Create the Bre-B to be linked to the account and the QR Codes for in-store or online purchases.
- Webhooks can be configured per account for real-time notifications (coming soon).
Semi-decentralized (Platform-Managed) Model
El proveedor de la plataforma (p. ej., un gateway de pagos) puede acceder y gestionar cuentas de comercio a través de varias sucursales o clientes.
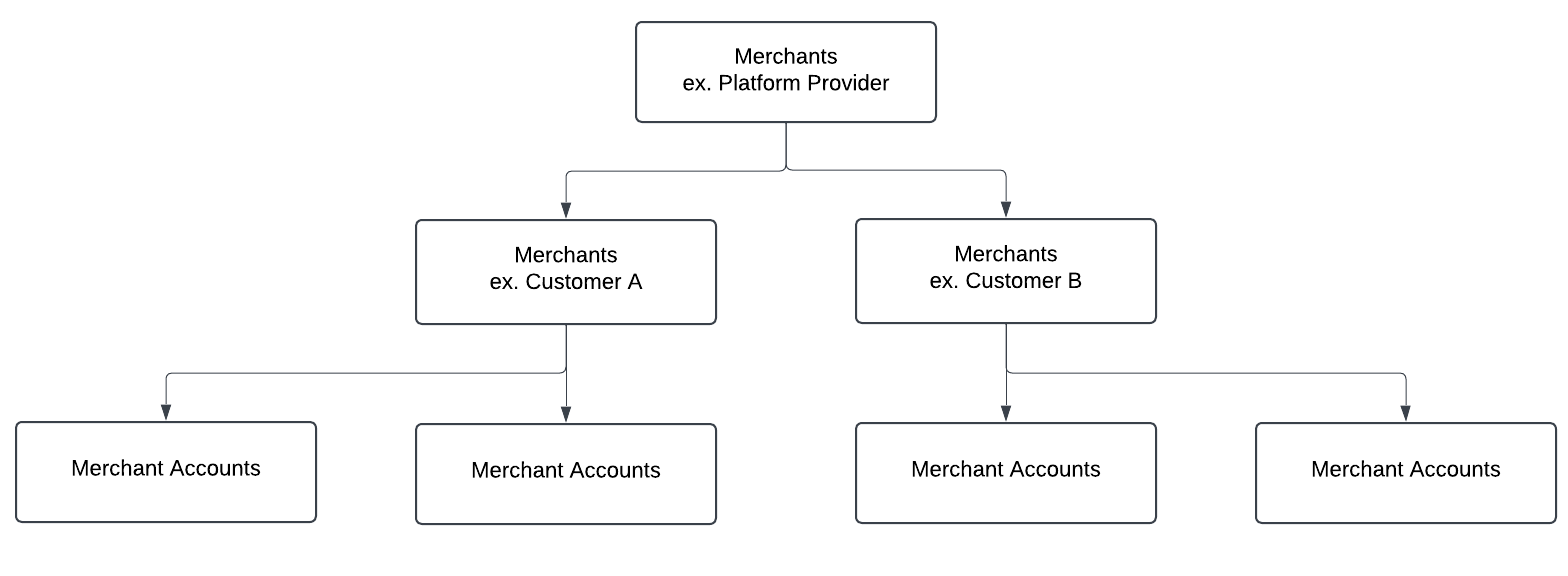
Semi-decentralized Model Diagram
Example: Semi-decentralized Model
- Platform provider manages the merchant accounts on behalf of a customer or several.
Implementation Notes:
- Platform provider uses its credentials to onboard merchants or sub-merchants..
- Merchant accounts are still created per branch.
- Webhooks can be configured per account for real-time notifications (coming soon).
- Create a merchant entity using the Create Customer endpoint.
- Create the Bre-B to be linked to the account(s) and the QR Codes for in-store or online purchases.
- Link a dedicated merchant account using Link Account.
Aggregator Model
A single merchant entity, such as a payment gateway (Aggregator), is responsible for managing multiple payment accounts internally. While only one customer entity is created with its own profile, the system allows for the creation of one or more merchant accounts.
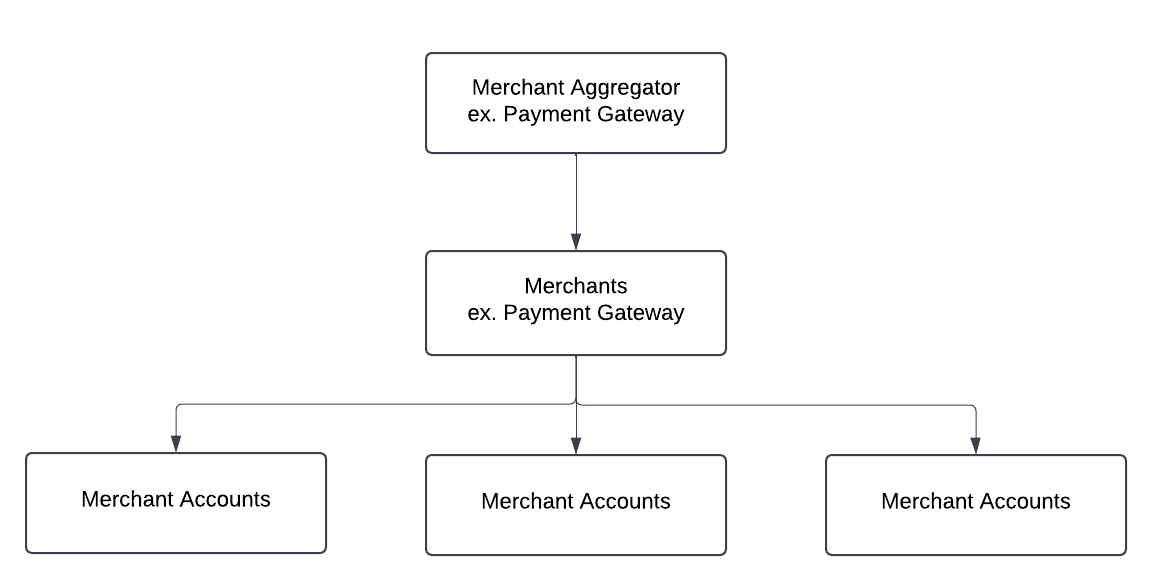
Aggregator Model Diagram
Example: Aggregator Model
- A single merchant entity, referred to as an Aggregator, manages multiple payment accounts within its internal structure.
- Often used by marketplaces or super-apps.
Implementation Notes:
- Only one customer entity is created (its own profile).
- One or more merchant accounts can be created.